The figure below shows a servo motor control circuit made of a power operational amplifier LM675. The motor uses a DC servo motor. As can be seen from the figure, the power operational amplifier LM675 is powered by 15V, the 15V voltage is applied to the non-inverting input of the operational amplifier LM675 via RP1, and the output voltage of the LM675 is applied to the input of the servo motor. A speed signal generator is mounted on the motor for detecting the speed of the motor in real time. In fact, the speed signal generator is a generator whose output voltage is proportional to the speed. The voltage outputted by the speed measuring signal generator G is fed back to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier as a speed error signal via the voltage dividing circuit. The voltage value set by the speed command potentiometer RP1 is divided by R1.R2 and applied to the non-inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier, which is equivalent to the reference voltage.
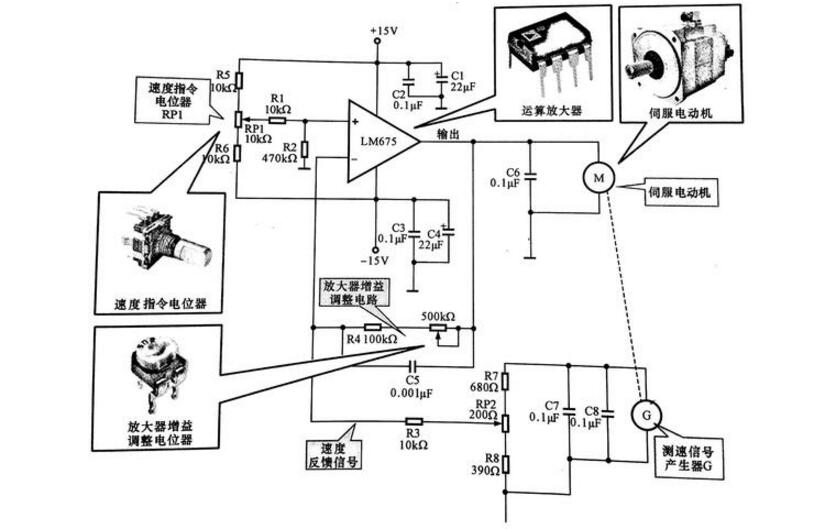
Servo motor control schematic
The servo motor uses the letter M to indicate the servo motor and is the source of power for the drive system. Operational Amplifier: Represented by the circuit name, LM675, is an amplifying component in the servo control circuit that provides the drive current for the servo motor.
Speed ​​command potentiometer RP1: Set the reference voltage of the operational amplifier in the circuit, that is, the speed setting. Amplifier Gain Adjusting Potentiometer RP2: Used to fine tune the gain and speed feedback signals of the amplifier in the circuit. When the load of the motor changes, the voltage fed back to the inverting input of the operational amplifier also changes, that is, the power
When the motive load is increased, the speed is reduced, and the output voltage of the tachometer generator is also lowered, so that the voltage at the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier is lowered, the difference between the voltage and the reference voltage is increased, and the output voltage of the operational amplifier is increased. Conversely, when the load becomes smaller and the motor speed increases, the output voltage of the speed measuring signal generator rises, the feedback voltage applied to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier increases, the difference between the voltage and the reference voltage decreases, and the output voltage of the operational amplifier decreases. This will cause the speed of the motor to drop, so that the speed can be automatically stabilized at the set value.
Servo motor advantages1. Accuracy: realizes closed-loop control of position, speed and torque; overcomes the problem of stepping motor out of step;
2, the speed: high-speed performance is good, the general rated speed can reach 2000 ~ 3000 rpm;
3. Adaptability: It has strong anti-overload capability and can withstand three times the rated torque. It is especially suitable for occasions with transient load fluctuations and quick start.
4. Stable: It runs smoothly at low speed, and does not produce stepping operation similar to stepper motor when running at low speed. Suitable for occasions with high speed response requirements;
5. Timeliness: The dynamics of motor acceleration and deceleration are short, generally within tens of milliseconds;
6, comfort: heat and noise are significantly reduced.
The specifications of each type of servo motor have parameters such as rated torque, maximum torque and servo motor inertia. There must be a correlation between each parameter and the load torque and load inertia. The output torque of the servo motor should be in accordance with the load. The motion conditions of the mechanism, such as the speed of the acceleration, the weight of the mechanism, the movement mode of the mechanism (horizontal and vertical rotation), etc.; the motion condition is not directly related to the output power of the servo motor, but the higher the output power of the servo motor is, the relative output is turned. The moment will be higher.
Therefore, not only the weight of the mechanism will affect the selection of the servo motor, but also the movement conditions will change the selection of the servo motor. When the inertia is larger, the larger the acceleration and deceleration torque are required, and the shorter the acceleration and deceleration time, the larger the servo motor output torque is required. When selecting the servo motor specifications, follow the steps below.
(1) Defining the requirements of the motion conditions of the load mechanism, that is, the speed of acceleration/deceleration, the speed of movement, the weight of the mechanism, and the movement mode of the mechanism.
(2) Calculate the load inertia of the mechanism by selecting the appropriate load inertia calculation formula according to the operating conditions.
(3) Select the appropriate false selected servo motor specifications based on the load inertia and the servo motor inertia.
(4) Calculate the acceleration torque and the deceleration torque in combination with the servo motor inertia and load inertia of the primary selection.
(5) Calculate the load torque according to the load weight, configuration, friction coefficient, and operating efficiency.
(6) The maximum output torque of the primary servo motor must be greater than the acceleration torque + load torque; if the conditions are not met, other models must be used for verification until the requirements meet the requirements.
(7) Calculate the continuous instantaneous torque based on the load torque, the acceleration torque, the deceleration torque, and the holding torque.
(8) The rated torque of the primary servo motor must be greater than the continuous instantaneous torque. For example, if the condition is not met, other models must be used for verification until it meets the requirements.
(9) Complete the selection.

When servo motor is selected, the first thing to consider is the choice of power. Generally pay attention to the following two points:
1. If the motor power is chosen too small. There will be a phenomenon of “small horse-drawn cartsâ€, causing the motor to be overloaded for a long time, causing its insulation to be damaged by heat, or even the motor being burnt.
2. If the motor power is selected too large. There will be a phenomenon of “large horse-drawn carâ€, whose output mechanical power cannot be fully utilized, and the power factor and efficiency are not high, which is not only bad for users and the power grid. It also causes a waste of electricity.
In other words, the motor power can neither be too large nor too small. To correctly select the power of the motor, the following calculations or comparisons must be made:
P=: F*V/100
(where P is the calculated power, the unit is KW, F is the required pulling force, the unit is N, V ​​is the working machine line speed m/s)
Also. The most common is to use analogy to select the power of the motor. The so-called analogy method is to compare the power of a motor used in a similar production machine.
The specific method is to know how much power the similar production machinery uses in this unit or other nearby units, and then use a similar power motor for the test. The purpose of the test is to verify that the selected motor matches the production machine.
The verification method is to make the motor drive the production machinery, measure the working current of the motor with a clamp-type ammeter, and compare the measured current with the rated current marked on the motor nameplate.
If the actual working current of the electric machine is not much different from the rated current indicated on the spleen, it indicates that the power of the selected motor is appropriate.
If the actual operating current of the motor is about 70% lower than the rated current indicated on the nameplate. It means that the power of the motor is too large, and the motor with less power should be exchanged.
If the measured motor current is more than 40% larger than the rated current indicated on the nameplate. It means that the power of the motor is too small, and the motor with higher power should be replaced.
In fact, it should be considered the torque (torque), motor power and torque calculation formula.
That is T=9550P/n
In the formula:
P-power, kW; n-motor rated speed, r/min; T-torque, Nm.
The output torque of the motor must be greater than the torque required by the working machine, generally requiring a safety factor.
Mechanical power formula: P=T*N/97500
P: power unit W; T: torque, unit gram / cm; N: speed, unit r / min.

1. Some systems, such as conveyors, lifting devices, etc., require the servo motor to stop as soon as possible. In the event of a fault, an emergency stop, or a power failure, the servo is not regeneratively braked and cannot decelerate the motor. At the same time, the mechanical inertia of the system is large. At this time, the dynamic brake should be selected according to the weight of the load and the working speed of the motor.
2. Some systems need to maintain the static position of the mechanical device, and the motor needs to provide a large output torque, and the stopping time is longer. If the self-locking function of the servo is used, it will often cause the motor to overheat or the amplifier to be overloaded. In this case, the motor with electromagnetic brake should be selected.
3. Some servo drives have a built-in regenerative braking unit. However, when the regenerative braking is frequent, the DC bus voltage may be too high. In this case, a regenerative braking resistor is required. Whether the regenerative braking resistor needs to be equipped separately, and how big it is, can refer to the instructions for use of the corresponding sample.
4. If a servo motor with an electromagnetic brake is selected, the moment of inertia of the motor will increase, and consideration should be given when calculating the torque.
Piezoelectric Ceramic Actuator Plate,Piezoelectric Bending Ceramic,Piezo Ceramic Diaphragm
NINGBO SANCO ELECTRONICS CO., LTD. , https://www.sancobuzzer.com
