"Face detection is a technique used to identify the location of a face within an image. The input to a face detection algorithm is typically an image, and the output consists of a sequence of bounding box coordinates that represent detected faces—ranging from zero to multiple faces. These bounding boxes are generally square-shaped and aligned upright, although some advanced methods may output rotated or rectangular bounding boxes depending on the orientation of the face.
A typical face detection process involves scanning the image for potential face regions and then classifying each candidate region as either a face or not. This two-step approach—scanning and classification—means that the speed of the algorithm depends on factors such as image size, complexity, and the number of faces present. To optimize performance, developers often adjust parameters like input image resolution, minimum face size, or maximum number of faces to detect.
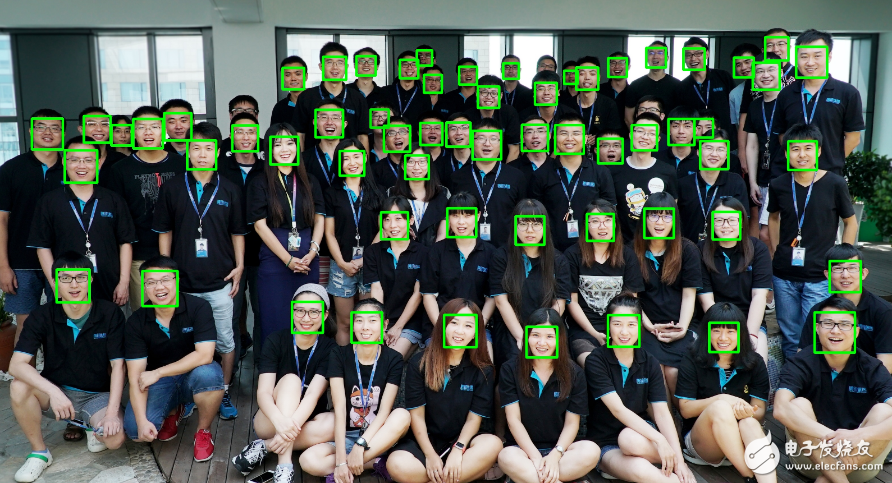

Figure 1: Example of face detection results (green box is the result of face detection).
Face registration, also known as facial landmark detection, refers to the process of identifying key points on a face, such as the eyes, nose, mouth, and other facial features. The input to a face registration algorithm includes a face image along with the face bounding box, and the output is a set of coordinates representing these key points. These points can vary in number, with common configurations including 5, 68, or 90 points, depending on the level of detail required.
Modern face registration techniques are often based on deep learning frameworks. They use the detected face region, scale it to a fixed size, and then estimate the positions of the key points. Because this process is relatively efficient, especially when compared to face detection, it is commonly used as a preprocessing step in more complex facial recognition systems.
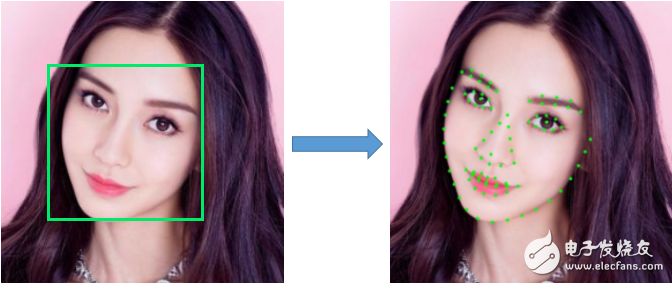
Figure 2: Example of face registration result (green point registration result on the right).
Face attribute recognition involves determining various characteristics of a face, such as gender, age, pose, and expression. The input usually includes a face image and the corresponding facial keypoint coordinates. The algorithm aligns the face based on these points and then performs attribute analysis. Traditional methods treat each attribute as a separate task, but recent advances in deep learning allow for multi-task learning, where multiple attributes can be predicted simultaneously.
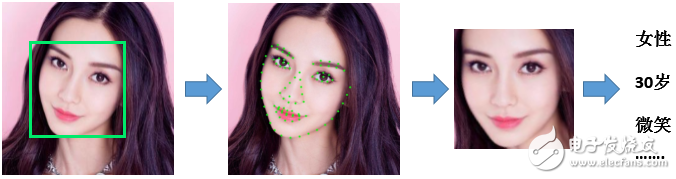
Figure 3: Face attribute recognition process (the rightmost text is the attribute recognition result).
Face feature extraction is the process of converting a face image into a fixed-length numerical representation, known as a "face feature." This feature vector captures unique characteristics of the face and can be used for comparison purposes. The input to this process includes a face image and its keypoint coordinates, which are used to align the face to a standard format before computing the feature.
In recent years, deep learning has become the dominant approach for face feature extraction. While early models were large and slow, modern architectures have been optimized for efficiency, making them suitable for deployment on mobile and embedded devices without significant loss of accuracy.
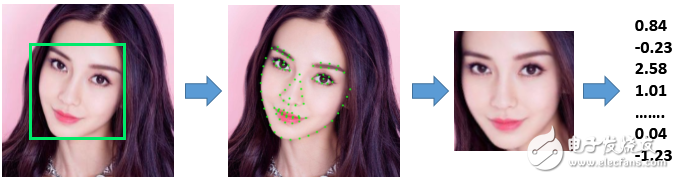
Figure 4: Face feature extraction process (the rightmost value string is “face featureâ€).
Face comparison, which includes tasks such as face verification, recognition, retrieval, and clustering, is the process of measuring the similarity between two face features. This is typically done using distance metrics like Euclidean or cosine similarity. Face comparison algorithms are fundamental to applications such as biometric authentication, identity verification, and large-scale face search systems.
By combining face detection, registration, attribute recognition, feature extraction, and comparison, modern facial recognition systems offer powerful tools for security, user identification, and personalized services in a wide range of industries."
ZHOUSHAN JIAERLING METER CO.,LTD , https://www.zsjrlmeter.com
