1 Overview
China's lighting electricity consumption accounts for about 12% of the total electricity consumption of the whole society, and road lighting electricity accounts for about 20% to 30%. With the implementation of the national highway network plan "7918", the peak of mountain highway construction has been ushered in. As a part of the road, the tunnel is indispensable for day and night in order to ensure the safety and comfort of driving. Therefore, the electricity and electricity charges for tunnel lighting account for a large proportion of the highway operating costs. With the increasing global energy supply, the state has introduced relevant policies to encourage energy conservation and emission reduction in the whole society. Tunnel lighting is an important part of the energy consumption of highway operation. How to use high-performance, low-energy light source to become a highway operation Whether it is the key to energy saving and emission reduction.
2 road tunnel lighting system
The particularity of highway tunnel lighting is reflected in the fact that the visual phenomena appearing in tunnel lighting are significantly different from the visual phenomena encountered in standard road lighting, mainly reflected in the daytime, daylight, daylight, and the brightness inside and outside the tunnel is extremely different. It is unrealistic to completely eliminate this difference from the perspective of economic and technical considerations. It can only be rationally designed according to the human eye's adaptability to light, providing a good visual environment to ensure the tunnel traffic environment is comfortable and safe. Road tunnel lighting is divided into basic lighting and reinforced lighting. The basic lighting mainly guarantees the lighting and night lighting of the basic section of the tunnel. The enhanced lighting is mainly to meet the needs of daytime lighting visual adaptability.
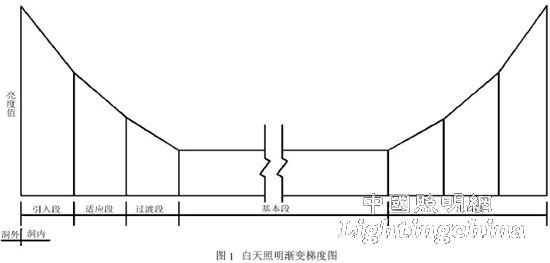
The purpose of tunnel lighting is to control the brightness of the luminaire to adjust the brightness to the range of the human visual adaptation curve, to reduce the sharp changes in brightness, and to ensure the safety and comfort of driving. To this end, tunnel lighting is usually divided into an introduction section, a transition section, a basic section and an exit section (see Fig. 1).
2.1 Black hole effect and dark adaptation when entering the tunnel
During the daytime, due to the large difference in brightness in the tunnel outside the tunnel, when the tunnel is observed from outside the tunnel, the tunnel entrance presents a black hole. During the process of driving the car from the bright outside into the tunnel, the ambient brightness is reduced from n×103cd/m2 to n×10-1cd/m2 in a few seconds. The eyes will have a short-term disability, and the physiological adaptation will go through a period of time. Time can see the internal situation of the tunnel, that is, “adapt to the hysteresisâ€.
2.2 Tunnel middle section lighting
After the driver drives through the entrance section and the transition section, the driver's vision completes the dark adaptation process. Next, the task of the middle section lighting is to ensure the parking line of sight in the tunnel. The lighting level in the middle section is related to factors such as air permeability (ie ventilation conditions), driving speed and traffic volume. As a closed structure inside the tunnel, in order to ensure the safety of driving, a reasonable maintenance of brightness is required, which can ensure the safety of driving, but not much waste of electric energy. In addition, factors affecting comfort have many other factors besides brightness, such as light color, lighting arrangement, point source or line source, which will affect the driver's subjective feeling.
There is no such strong darkness problem during the day and the traffic volume is greatly reduced, so the lighting standard can be appropriately reduced. The degree of reduction is limited to the absence of traffic accidents, and the general reduction factor may be 0.5. At night, the entire length of the tunnel is illuminated according to the same standard. While ensuring the brightness of the road surface, it is also necessary to ensure that the side wall has sufficient brightness, and the wall material with a reflectance of not less than 0.7 should be laid in the range of 2 m of the side wall. Through bicycles and pedestrian tunnels, take care to avoid the dangers of bicycles and pedestrians passing through the dark passages and possible dangers.
2.3 Tunnel exit section lighting
In a one-way traffic tunnel, it is sometimes necessary to properly treat the exit section in order to mitigate the adverse effects of the white hole phenomenon. For example, when the exit hole is an open environment, when facing the sea, facing the high brightness such as snow mountains and forming glare, the exit should be reinforced, otherwise there is no need to enhance the lighting.
In the two-way traffic tunnel, both ends are entrances and exits, and the illumination at both ends is exactly the same, so there is no problem of lighting treatment of the exit section.
The glare problem in the exit section refers to the east or west exit, where sunlight may penetrate directly into the tunnel during sunrise or sunset, creating a strong direct glare. In order to avoid this phenomenon, the exit should be properly treated. There are two main methods: setting the curve in the exit section of the hole, or not setting the curve section outside the hole and occluding it. The former does not directly penetrate the tunnel after the curve is set in the exit section. Even if there is incident sunlight, it will illuminate the wall. After reflection, the brightness of the exit section can be increased, so that the driver can clearly adapt to the brightness conditions and time. If the curve is set, the exit direction is ideal for a mountain. The latter set a curve on the exit approach road, and set a retaining wall on the outside of the curve, planting tall evergreen trees, etc., blocking direct sunlight. Due to the existence of the above-mentioned phenomena, this puts higher requirements on tunnel lighting. It is necessary to maximize the elimination of undesirable phenomena by setting reasonable partitions, selecting appropriate light sources, and adopting appropriate lighting arrangements to ensure a good Driving environment.
