Data communication refers to the process of transferring information between devices. To ensure seamless interaction, protocols are established to define the rules and procedures for communication. These protocols allow the sender and receiver to coordinate effectively. At the physical layer, data is converted into signals that can be transmitted through wired media like copper or fiber optic cables, or wireless media such as radio or infrared. Higher-level protocols handle tasks such as encapsulation, flow control, and error recovery to ensure reliable transmission.
A communication protocol can be compared to a diplomatic agreement in an embassy. Just as diplomats at different levels manage various types of agreements and interact with counterparts from other embassies, communication protocols operate in a layered structure. Each layer handles specific aspects of communication, working together to enable smooth data exchange. Figure D-2 provides a simplified view of this hierarchical network structure.
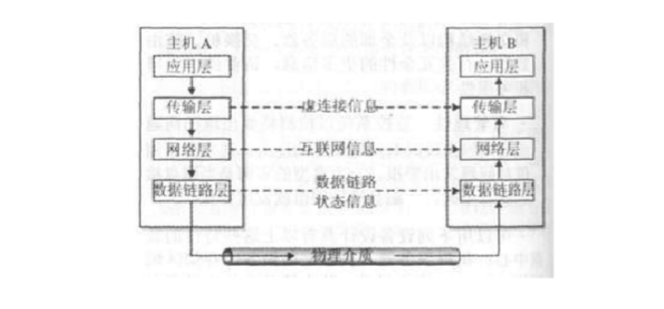
Figure D-2: Schematic diagram of hierarchical network structure
In 1979, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) introduced the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, which organizes network communication into seven layers—physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application. Each layer has defined functions and interactions with adjacent layers. Although the OSI model never became a widely adopted standard, it remains a useful framework for understanding how protocols are structured.
What is a data communication protocol?
A data communication protocol, also known as a data communication control protocol, is a set of rules that ensure effective and reliable communication between two parties in a data network. These rules cover data format, transmission order, speed, confirmation, error detection, retransmission, and more. There are two main types: basic character-based protocols, such as BSC (Binary Synchronous Communication), and advanced bit-based protocols like HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control) and SDLC (Synchronous Data Link Control).
Characteristics of Data Communication Protocols
Data communication protocols have two key features:
First, they follow a hierarchical structure. A network architecture is essentially a collection of communication layers and protocols. In an open system, each end system must implement the seven-layer OSI model, while relay systems handle the lower three layers.
Second, these protocols are standardized. They include both international standards, such as those from CCITT and ISO, and company-specific standards. CCITT recommendations like V-series, X-series, T-series, and I-series define protocols for telephone networks, data communication services, ISDN, and more.
Engineering Technology of Data Communication Protocols
The practical implementation of protocols involves several key technologies, including formal description, verification, analysis, and conformance testing.
1. **Protocol Formal Description Technology**
This technique uses formal languages or state diagrams to describe a protocol clearly and unambiguously. Standards like SDL, ESTELLE, and LOTOS have been developed by CCITT and ISO to facilitate this.
2. **Protocol Verification Technology**
Verification ensures that a protocol meets its specifications. Methods include state transition analysis, programming language-based verification, sequential logic, and algebraic approaches. Each method has its strengths and limitations depending on the complexity of the protocol.
3. **Protocol Analysis Technology**
This involves monitoring and simulating protocol execution to detect and correct errors. Tools like protocol analyzers help operators analyze real-time data and test device behavior under controlled conditions.
4. **Protocol Conformance Testing**
This tests how well a protocol implementation aligns with its standard. The goal is to enhance interoperability between data communication devices.
Guangzhou Winson Information Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.barcodescanner-2d.com
